Wednesday, March 29 2023
Did you know that “bad” weather can be really GOOD for gold prospectors? Of course no one ever hopes that Mother Nature causes catastrophic loss of life and property, but the ups and downs of weather events in any gold-bearing area are something to take advantage of. Nature can help all of us in our quest for the shiny stuff— especially in light of recent atmospheric rivers causing flooding and lots of snow in California, eastern Idaho, northeast Utah, northwest Colorado, the Cacade Ranges, portions of the northern and central Rockies, and portions of Arizona and Nevada.
How does this help you get more gold? Primarily, multiple weather events cause large amounts of gold to move and replenish areas that already have been worked. And even when the atmospheric rivers die down, the higher than normal snowpack will cause water levels in rivers to flow well into the summer instead of drying up in late spring. Higher water levels extend your mining season, and allow you to run high-production equipment such as highbankers and power sluices. Miners can also work stream bank deposits once the water recedes back to normal flows. Typical winter storms that regularly occur in gold-bearing areas usually do not create enough havoc to force substantial amounts of "new" gold into movement. However, when Mother Nature really goes to work as we’ve seen lately, a great deal of gold can be set free, creating a bonanza for gold hunters. Gold veins that have been hidden for decades suddenly can be exposed. Floods can also sweep gold out of abandoned mines and wash it downriver. Known gold digs can be washed out, trees uprooted, and the landscape eroded— all pluses for prospectors! When tons of rock, cobble, and boulders are swept downstream along bedrock during a huge storm, quite a bit of destruction occurs. Plants, weeds, and trees that normally grow along the river and gravel bars are washed away. And when a major storm or flood tears up large portions of a streambed, a fair amount of this newly-released gold, because of its weight, will be deposited along the riverbed and settle into cracks and crevices (hand dredges are an ideal tool in this situation).
Thursday, September 22 2022
Gold can hide down in the deepest part of a crack or crevice or behind a boulder and often is best reached with a hand dredge, also called a "sucker gun" or "suction gun." This gold prospecting tool is ideal for working below the water line when a motorized dredge cannot be used. It helps you get the gold out of some really tight spaces, a hand dredge is well, handy, when you're prospecting along a river. If you've found a rich spot that is hard to access, these two hand dredges can produce some decent gold! Also check out the many accessories that make your hand dredge even better!
Clamps are not necessary unless you plan to use the system in strong current and want to be extra cautious. For users in deeper water or stronger current, consider wrapping a leash around the lid and tie it off at your waist to prevent the bucket from breaking away.
The Quick Sniper is a tool that uses some new ideas to help you collect the hard-to-get gold from heavy sands under boulders, in crevices, and behind obstructions. The “NOZZLE” of the Quick-Sniper is where the magic happens. Inside the nozzle is a short white plastic pipe that extends into the tube. This allows you to pump the handle four or five times before you need to take steps to collect sand and gravel. Instead of pulling the handle and then ejecting the material into a pan or bucket after each pull, the cavity created inside the tube will hold your heavies, allowing water and the lightest material to swirl out and go back into the water before you pull again. Shaking the pump gently will transfer the heaviest of sands and gravel deeper into the cavity. Then, after you have repeated this action a few times, pull off the cap and dump the contents of the pump into your pan or bucket. The flexible tube extending from the end of the nozzle is designed to pull out, allowing you to extend the reach of the tube about 4-5 inches. If this tube is sliding too easily, wrap some electrical tape around the inner end, and it will be more secure within the Quick-Sniper.
|
|
Nugget of News Blog |






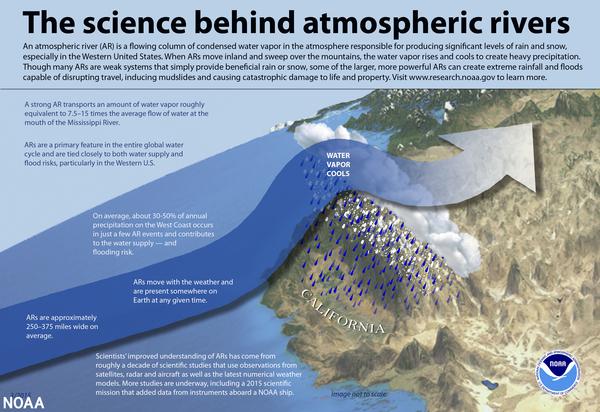 Atmospheric rivers are large, narrow sections of the earth's atmosphere that carry moisture from the earth's tropics near the equator to the poles. On average, the earth has four to five active atmospheric rivers at any time. A vast majority of atmospheric rivers happen in the fall and winter. The northern Pacific Coast receives the bulk of activity in the fall, and the California coast receives more in the winter. Since December 2022, the U.S. West has been slammed with back-to-back-to-back atmospheric rivers. These events provide as much as half of the region’s annual precipitation, bringing much-needed water to parched lands and adding to the snowpack in the high mountains. This year’s storms have done a lot to restore the landscape drought and is “greening up” the landscape and refilling many smaller reservoirs.
Atmospheric rivers are large, narrow sections of the earth's atmosphere that carry moisture from the earth's tropics near the equator to the poles. On average, the earth has four to five active atmospheric rivers at any time. A vast majority of atmospheric rivers happen in the fall and winter. The northern Pacific Coast receives the bulk of activity in the fall, and the California coast receives more in the winter. Since December 2022, the U.S. West has been slammed with back-to-back-to-back atmospheric rivers. These events provide as much as half of the region’s annual precipitation, bringing much-needed water to parched lands and adding to the snowpack in the high mountains. This year’s storms have done a lot to restore the landscape drought and is “greening up” the landscape and refilling many smaller reservoirs.
