Wednesday, March 29 2023
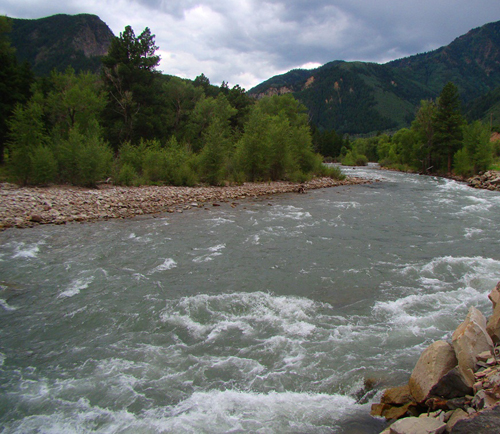
Did you know that “bad” weather can be really GOOD for gold prospectors? Of course no one ever hopes that Mother Nature causes catastrophic loss of life and property, but the ups and downs of weather events in any gold-bearing area are something to take advantage of. Nature can help all of us in our quest for the shiny stuff— especially in light of recent atmospheric rivers causing flooding and lots of snow in California, eastern Idaho, northeast Utah, northwest Colorado, the Cacade Ranges, portions of the northern and central Rockies, and portions of Arizona and Nevada.
How does this help you get more gold? Primarily, multiple weather events cause large amounts of gold to move and replenish areas that already have been worked. And even when the atmospheric rivers die down, the higher than normal snowpack will cause water levels in rivers to flow well into the summer instead of drying up in late spring. Higher water levels extend your mining season, and allow you to run high-production equipment such as highbankers and power sluices. Miners can also work stream bank deposits once the water recedes back to normal flows. Typical winter storms that regularly occur in gold-bearing areas usually do not create enough havoc to force substantial amounts of "new" gold into movement. However, when Mother Nature really goes to work as we’ve seen lately, a great deal of gold can be set free, creating a bonanza for gold hunters. Gold veins that have been hidden for decades suddenly can be exposed. Floods can also sweep gold out of abandoned mines and wash it downriver. Known gold digs can be washed out, trees uprooted, and the landscape eroded— all pluses for prospectors! When tons of rock, cobble, and boulders are swept downstream along bedrock during a huge storm, quite a bit of destruction occurs. Plants, weeds, and trees that normally grow along the river and gravel bars are washed away. And when a major storm or flood tears up large portions of a streambed, a fair amount of this newly-released gold, because of its weight, will be deposited along the riverbed and settle into cracks and crevices (hand dredges are an ideal tool in this situation).
Monday, July 30 2018
Places where gold naturally concentrates in an environment of streams and drainages are k When deciding where to start sampling, it’s helpful if you think of a river or stream as a sluice box. Waterways obviously don’t have aluminum riffles and matting, however, they do have natural gold traps that do the same thing that a sluice will do— allow gold to settle out of gravels and be caught while the bulk of the sands continue downstream. Heavy material such as gold doesn’t get spread along evenly, it is most likely caught in certain areas. The downstream parts of inside bends in a stream are favorable places to look for pay streaks. Just how good depends on how sharp the bend in the stream actually is. Usually the sharper the bend, the better the pay streak. If a tributary is known to have coarse gold, look at the intersection of the tributary and the main channel. Behind an obstruction (large boulder, an island, or an outcrop of bedrock) is another good place to look for a pay streak. Boulders and other obstructions can create turbulence where ordinarily smooth flowing water turns into fast flowing whitewater. It is between the fast white water and the quiet dark water that gold drops out. The coarsest gold tends to be found on the outer parts of the pay streak, and the finer-sized gold is on the inner part of the pay streak. When you are working, if it seems as if the streak is petering out as you go toward the middle of the water flow because you are finding little gold, this region of the pay streak is often where the biggest number of nuggets are most likely to occur. Once you know where paystreaks form, you might wonder if they are more likely found on bedrock or in gravels. They are nearly always found on bedrock or some sort of false bedrock. False bedrock might include caliche, a clay layer, or just a well-packed hard pan. You may just get lucky and hit something great with your first shovel of dirt, but more likely you’ll need to test a few different places. Even very experienced prospectors need to keep testing to find those hotspots and paystreaks. Good luck and keep sampling! Saturday, December 02 2017
You might have heard the term “flood plain gold” and are wondering what it really means. A very simple definition is “fine-sized gold flakes carried or redistributed by flood waters and deposited on gravel bars as the flood waters recede.” When this “redistribution” occurs, it is usually after heavy winter storms that churned up rivers enough to turn part of the bedload over and move the river bar gravels from one place to another. Within these gravels is fine gold that was previously deposited there. When waterways flow way up and above their normal banks, they generally drop the heavier gold in the front of the bar, and as pressure decreases, the finer gold starts dropping into the mixed gravel. Over time, some of this finer gold will work its way down to bedrock, but generally it stays on the move.
How did the gold get there in the first place? There are many classifications of placer deposits, and their definitions can provide the answer. Among the most well-known is stream placers. Streams carry gold from eroded veins and concentrate them in various ways. Modern streams refer to present-day gold-bearing waterways that are the most common sources of gold for today’s prospectors. Tertiary and intervolcanic channels are rivers buried from mud and volcanic flows that existed prior to our modern-day waterways. High benches were created as rivers cut their way deeper into the bedrock and could be located hundreds of feet above today’s modern rivers. Desert placers are generally the result of torrential flash flooding and not a constant water flow. Glacial stream deposits are created by melting glaciers that can concentrate gold if the water flow is sufficient. Marine or beach deposits can come from wave action against cliffs, from off-shore currents bringing in gold-bearing material from under the ocean, or even from gold-bearing streams that flowed into the beach area eons ago. Since there is a strong possibility that gold can get moved around during storms, it’s now important to know WHERE to find this “dropped out” gold. The secret is to find that drop point and to capitalize on its accumulation. Fine gold looks fantastic in a pan or box, but its weight can be deceivingly light. It takes a lot of fine gold to be equal to a larger piece and to have enough weight to make the recovery effort worthwhile. Some of the best areas to look for flood plain gold are where the stream or river widens out, or levels out, or changes direction. The inside of a bend is good. Rocks and weeds and small shrubs are also potentially good collection spots. When checking out collection spots, be extra careful. Calm water on the surface can hide swift currents underneath. Keep in mind that the effects of heavy winter rains and snow will not be the same on all waterways. Redistribution might occur to a larger degree on larger rivers. Or it could be the opposite where you live and prospect. No one hopes for an especially “bad winter,” but if Mother Nature makes it so, this information could be the silver lining— a way to turn lemons into lemonade come spring when you can get out and take advantage of any gold redistribution that occurs. Good luck and be safe! Nugget of News Blog |
|
Nugget of News Blog |






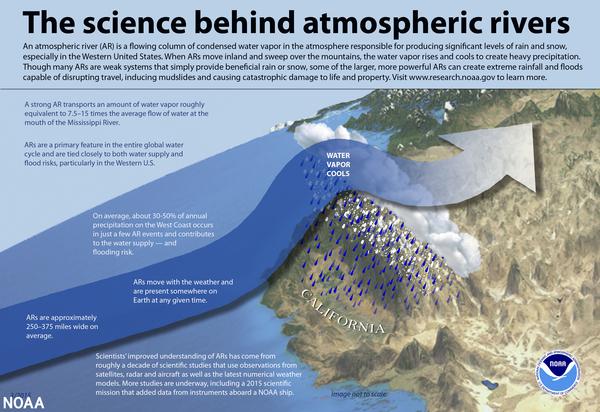 Atmospheric rivers are large, narrow sections of the earth's atmosphere that carry moisture from the earth's tropics near the equator to the poles. On average, the earth has four to five active atmospheric rivers at any time. A vast majority of atmospheric rivers happen in the fall and winter. The northern Pacific Coast receives the bulk of activity in the fall, and the California coast receives more in the winter. Since December 2022, the U.S. West has been slammed with back-to-back-to-back atmospheric rivers. These events provide as much as half of the region’s annual precipitation, bringing much-needed water to parched lands and adding to the snowpack in the high mountains. This year’s storms have done a lot to restore the landscape drought and is “greening up” the landscape and refilling many smaller reservoirs.
Atmospheric rivers are large, narrow sections of the earth's atmosphere that carry moisture from the earth's tropics near the equator to the poles. On average, the earth has four to five active atmospheric rivers at any time. A vast majority of atmospheric rivers happen in the fall and winter. The northern Pacific Coast receives the bulk of activity in the fall, and the California coast receives more in the winter. Since December 2022, the U.S. West has been slammed with back-to-back-to-back atmospheric rivers. These events provide as much as half of the region’s annual precipitation, bringing much-needed water to parched lands and adding to the snowpack in the high mountains. This year’s storms have done a lot to restore the landscape drought and is “greening up” the landscape and refilling many smaller reservoirs.