Tuesday, July 01 2014
Like most gold regions that boomed in the 1800s, Colorado’s Cripple Creek Mining District came from humble beginnings. Little more than cattle roamed the high valleys perched nearly two miles above sea level, and prior to ranching, generations of Ute Indians had lived off the land. But unlike most boomtowns, the gold never completely ran out here, and it continues to be mined successfully today. Historically, the Cripple Creek Mining District has produced over 24 million troy ounces of gold, along with some silver. That amount exceeds the combined production of the California and Alaska Gold Rushes! The millions made from 1891 through the present has earned it the distinction of “The World’s Greatest Gold Camp.” Today, the district is not only filled with gold rush era buildings and mining relics, but you can also tour real mines, visit interesting museums, ride the rails of a narrow gauge train, hike and bike while admiring mountain scenery, and even gamble on Lady Luck at the casinos. Pikes Peak Gold RushThe Pikes Peak Gold Rush officially began in 1859, a decade after the California Gold Rush. At that time, the land was still part of the Kansas Territory. The first color was actually found a few years earlier in 1850 at the confluence of Ralston and Clear Creeks, but John Ralston was California-bound, so the shiny stuff stayed where it lay… for a while. Several prospecting parties returned to Ralston Creek in 1858 and 1859, but didn’t find much. In fact, many were so discouraged that they didn’t stick around. The dedicated prospectors who persevered referred to those who gave up as the “Go Backers.” Soon enough, though, a few productive placer deposits were found along the South Platte River at the base of the mountains, the canyon of Clear Creek in the mountains west of Golden, and South Park. Word spread of these glittering discoveries, and “Pikes Peak or Bust” became a popular mantra. During the next several years, 100,000 gold-seekers headed for Colorado; 50,000 completed the journey; half of those became “Go Backers” and the remaining 25,000 turned a territory into a state in 1876. Cripple Creek Gold RushMost of the initial easy-to-reach gold deposits were largely played out by 1863, but then ranch hand Robert Womack started an even bigger gold rush. He found the shiny stuff in Cripple Creek in 1890, causing thousands of prospectors to head to the southwest slopes of Pikes Peak. Sadly, Womack died penniless several years later, even though his El Paso claim, which he sold for $500 and a bottle of liquor, produced millions of dollars in gold for the buyer. Between 1894 and 1917, over 500 mines operated in the Cripple Creek Mining District, which also included the thriving town of Victor. Headframes and other relics from many of those historic mines have been preserved, so it’s easy to get a good look up close. Perhaps one of the reasons it took 30 years for gold to be found in Cripple Creek following the state’s first gold rush is because no one expected gold, especially not millions of ounces, to be in this area. Most of the old-timers’ theories about how to locate gold just didn’t hold up here. Modern geologists know that areas that were highly volcanic in prehistoric times, are likely places to create rich underground deposits. The six square miles that comprise the Cripple Creek & Victor Mining District are located in the caldera of an extinct volcano. From what one frustrated miner wrote in Cripple Creek Illustrated, some early prospectors were stumped by the gold in this region: “Geographically, Cripple Creek is a freak. It is erratic, eccentric, and full of whims and caprices. That is, it is so to the man of science and the miner of experience. It is a vast crater bed in which the elements once were wont to make merry with nature and play unexpected pranks… The veins run here, there, and everywhere, cutting in all directions and even violating the theory that to have real value the vein should strike toward the poles of the earth.,, the experience has been that the deeper down into the earth the shafts penetrate, the richer is the ore, and the wider, more solid, and enduring the deposits.” Sunday, June 01 2014
At the consolidated court hearings held in San Bernardino County in California on May 1, Judge Gilbert Ochoa heard arguments from attorneys David Young and James Buchal on behalf of the miners. He had already received all the supporting documents and arguments from each of the involved parties. One of the key questions Judge Ochoa asked of attorneys representing the State of California was if they could provide a date when the current moratorium will end. The answer was, "No, Your Honor." Saturday, May 03 2014
The abbreviation kHz stands for ”kilohertz” which is the measurement of radio frequency radiation. A Hertz is the unit of measurement for counts per unit of time. Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. The higher the frequency, the more waves travel through space during a given time
PI (pulse induction) detectors work a bit differently by putting magnetic field energy into the ground and then switching off and waiting a short period before they start to look for a response. This makes them better at handling ground mineralization than a VLF machine because during that short delay the magnetic response of iron trash minerals that you don't want to find dies out, but the signal from tiny bits of buried gold does, too. VLF detectors are more sensitive to finding the smallest bits of gold, but do not as easily cancel out ground mineralization. If you've been shopping for a metal detector, you might have noticed that the manufacturers list the kHz of each machine. But how do you know if a higher or lower frequency is better? In most situations, a few kHz one way or the other will have a negligible impact on performance out in the field. The importance of frequency is most noticed when you are hunting for one particular type of treasure over another. For example, if you are coin shooting at the park, you can opt for a lower frequency metal detector which will cost less. However, if your main objective is to find gold nuggets with your detector, consider a higher frequency machine such as the Fisher Gold Bug 2 or Garrett AT Gold. Tuesday, April 01 2014
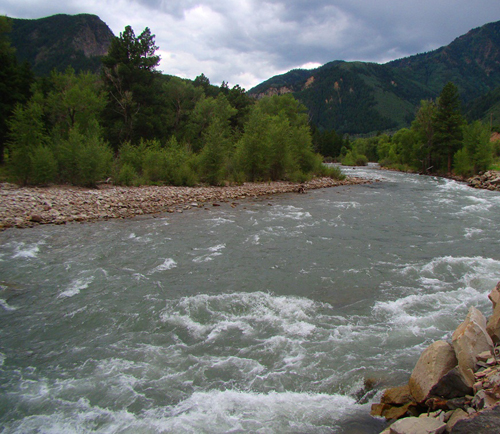
Typical winter storms that regularly occur in gold country usually do not create enough havoc to force substantial amounts of "new" gold into movement. However, when major flooding like what happened in Colorado in September of 2013 is followed by a “bad” winter, a great deal of gold can be set free. When tons of rock, cobble, and boulders are swept downstream along bedrock during a huge storm, quite a bit of destruction occurs. Plants, weeds, and trees that normally grow along the river and gravel bars are washed away. And when a major storm or flood tears up large portions of a streambed, a fair amount of this newly-released gold, because of its weight, will be deposited along the riverbed and settle into cracks and crevices. Saturday, March 01 2014
Natural Factors to Consider Before Digging for Gold:
Saturday, February 15 2014
Among the many improvements made to mining technology during the Industrial Revolution, perhaps the most important involved drilling and blasting. In the early days, black powder, a relatively low-power explosive was the only blasting agent available. To use it, holes had to be pounded into rock by hand. Working in teams of two, one miner would hold a pointed steel chisel while the other hit it with a sledge hammer. Each hole had to be hand drilled to six or eight inches in depth. Needless to say, this was slow, tedious, and tiring work. During a 10-hour shift, a team could typically drill, load, and fire black powder charges in only eight or 10 holes. Depending on the size of the mine tunnel, that single blast could bring down three quarters to two and a half tons of rock. Dynamite, an explosive five times more powerful than black powder, was invented in 1866 by Swedish chemist, Alfred Bernhard Nobel (the Nobel Prizes awarded today were named after him). Nobel held 350 different patents; dynamite is his most famous claim to fame. By the mid 1870s, dynamite had largely replaced black powder in the mines.
Unfortunately, thousands of hard rock miners died before J. George Leyner of Denver, Colorado invented a better machine drill that all but eliminated deadly silicosis. The improved drill forced water into the drill hole and created a harmless mud out of the drill shavings. The mud acted as a very efficient wet grinding compound while also cooling the drill bit, and the flow of water flushed out the drill hole. Leyner patented his mechanism in 1897. This type of drill hasn’t changed much over the years, and is still used in modern-day hard rock mines. Sunday, February 02 2014
According to a recent article posted on foxnews.com, a mining supply company located in Auburn, California reported that business has been up by 10 percent. The boon in business is because in Placer County, rivers have dropped to historically low levels, opening new possibilities for prospectors. "Stuff that's normally submerged in water is now available," said James Hutchings, Sacramento chapter president of the Gold Prospectors Association of America. "The exposed cracks and crevices can hold chunks of gold that have washed down from the mountains." If you are heading to Auburn hoping to spot something shiny, also take some time to enjoy Old Town and learn the area's rich gold mining history. California State Highway 49, also known as the Gold Rush Highway, winds its way through a nine-county area that in the mid 1800s was home to more than 2,500 gold mining camps. Most of those camps disappeared after the gold ran out, but a few communities survived and even thrived. Auburn is one such city. There are over 60 restaurants, taverns, antique shops, art galleries, and unique specialty stores in Old Town. Check out the irregular shaped post office on Lincoln Way. It dates to1857 and was built directly over a branch of the Auburn Ravine (a stream still flows directly below). This post office is the oldest one in California housed in its original building, and is also the oldest continually operated post office west of the Mississippi. If Old Town seems vaguely familiar to you, it’s because it was featured in the 1996 film Phenomenon starring John Travolta, Kyra Sedgwick, Forest Whitaker and Robert Duvall. The crew filmed for a month in the fall of 1995 on Sacramento Street, as well as at places such as a bar, apple orchard, county courthouse, a park, and a lawyer's office. Roughly 125 million ounces of gold were taken from the hills in California’s famed “Gold Country” during the Gold Rush. Auburn was lucky in that it survived the boom and bust cycles typical of early towns. Conveniently located at the junction of Interstate 80 and Highway 49, it’s easy to stop in and experience a bit of its golden history.
Before becoming one of Auburn’s most famous attractions (corner of Lincoln Way and Commercial Street), this 1891 red and white firehouse was home to the Auburn Volunteer Fire Dept., one of the oldest volunteer groups west of the Mississippi. Organized in 1852, this group is still fighting Auburn fires. The Placer County Courthouse at 101 Maple Street was completed in 1898 and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It also houses a FREE museum that presents an overview of Placer County history and a nice collection of Native American artifacts. One of the best exhibits is 194 ounces of raw gold mined from Placer County soil. Known as the Joss House, this structure at 200 Sacramento Street in Auburn, California was built after the fire of 1855. It served as a temple and house of worship for the area’s Chinese population. In the 1880s, this block of Sacramento Street was known as “Chinatown Hill.” The Chinese concentrated here and operated laundry shops, opium dens and card rooms. Brewery Lane, just north of the Joss House, was the entrance to Auburn’s “red light district.” During the district’s illustrious history, a pious man seeking to burn out the ladies also unfortunately burned out some of the Chinese settlement. Saturday, January 11 2014
For thousands of years, humans have been prospecting, mining and refining metals. The invention of smelting was a true technological advancement for mankind and marked the end of the Stone Age. Working with native metals such as copper, silver, gold, lead, and tin came first. These metals have fairly low melting points and the ability to cast and forge them was revolutionary. The Bronze Age was born when tin was mixed with copper, creating the first alloy and better weapons of war. Wednesday, January 01 2014
Mark your calendars to attend a Gold Show in 2014! Gold and Treasure Expos sponsored by the Gold Prospectors Association of America (GPAA) are open to the public. Admission is $5 for adults; free for kids under 12. Each paid attendee will receive a 14 inch GPAA Gold Catcher Gold Pan and a copy of Gold Prospectors, the GPAA’s national magazine. Also, the first 100 paid attendees will receive a free vial of real gold!
2110 Frear St. (541) 957-7010 Lancaster, CA 93536 (661) 206-0427 9777 Las Vegas Blvd. South Las Vegas, NV (866) 796-7111 110 9th Ave. SW Puyallup, WA 98371 (253) 845-1771 ALSO MARK YOUR CALENDARS for the... 2014 Gold Prospecting & Mining Summit After a hiatus last year, this Summit returns to the Eldorado County Fairgrounds and features 80 booths with the latest in prospecting and mining equipment. Sponsored by ICMJ's Prospecting and Mining Journal, a team of writers and experts will be on hand to provide you with the information you need to succeed at gold prospecting and gold mining. Lecture topics include:
And back by popular demand... Two Additional Days of Hands-on Training! Admission is $5 at the door. Fairgrounds charges $5 parking per day. No pre-registration required for the Mining Summit, but pre- registration is a good idea for the Hands-on Training classes. Sunday, December 01 2013
Dry washers are like highbankers except they do not use water to recover gold. While wet processing is nearly always faster and more efficient, especially for fine gold, dry washers are the best tool for recovering gold nuggets, pickers, and flakes from dry materials in the desert or other areas where water is not plentiful. Keep these tips and tricks in mind when using a dry washer: • Double-check all the "throw away" rocks. Scanning them with a metal detector is a great way to ensure you're not tossing aside gold-laden rocks. Also, don't assume old tailings piles have been totally worked out. This is another time to use a metal detector because ordinary rocks could be laced with gold and completely over-looked by earlier prospectors.
|
|
Nugget of News Blog |








 Around the same time period, pneumatic machine drills were first developed. Compressed air to power the drills was piped underground from large steam-powered compressors located at the surface. Machine drills could accommodate five to six foot drill steels that were capable of drilling three to four foot holes into sold rock in a matter of minutes. This new drill increased the tonnage of rock that could be blasted by two-man teams of miners to between four and 10 tons per shift. But, the new technology was not without hazards— namely the disease of silicosis. Machine drilling created clouds of razor sharp microscopic silica dust that miners breathed into their lungs. It took only a few years of operating this drill for a miner to develop this incurable disease.
Around the same time period, pneumatic machine drills were first developed. Compressed air to power the drills was piped underground from large steam-powered compressors located at the surface. Machine drills could accommodate five to six foot drill steels that were capable of drilling three to four foot holes into sold rock in a matter of minutes. This new drill increased the tonnage of rock that could be blasted by two-man teams of miners to between four and 10 tons per shift. But, the new technology was not without hazards— namely the disease of silicosis. Machine drilling created clouds of razor sharp microscopic silica dust that miners breathed into their lungs. It took only a few years of operating this drill for a miner to develop this incurable disease. 

 Drywashers are operated by shoveling gold-bearing gravels into an upper box which is covered with a screen. The larger rocks that are too big to pass through the screen slide off. Gravel small enough to go through is fed down into the lower gold recovery box, which is an inclined trough with cross riffles much like a sluice. The bottom of the recovery box consists of a thin, light-weight porous cloth. Beneath the riffle box is a blower that pulses air up through the cloth. The vibrations and air flow, combined with the shaking and classifying action of the dry washer allows the gold to settle to the bottom where it is captured in the riffles.
Drywashers are operated by shoveling gold-bearing gravels into an upper box which is covered with a screen. The larger rocks that are too big to pass through the screen slide off. Gravel small enough to go through is fed down into the lower gold recovery box, which is an inclined trough with cross riffles much like a sluice. The bottom of the recovery box consists of a thin, light-weight porous cloth. Beneath the riffle box is a blower that pulses air up through the cloth. The vibrations and air flow, combined with the shaking and classifying action of the dry washer allows the gold to settle to the bottom where it is captured in the riffles.