Tuesday, February 14 2023
There are a variety of searchcoil sizes and shapes and configurations. The correct one to use depends on the environment it will be CONFIGURATIONS Concentric Mono Imaging DD Search coils have two smaller “D” shaped coils housed inside to penetrate heavily mineralized ground that is commonly encountered while gold prospecting and relic hunting. The Double-D configuration is designed to
Monday, February 13 2023
The searchcoil is a vital part of your metal detector. It generates a magnetic field and senses metallic targets in the surrounding environment. The size and depth of the magnetic field is determined by the shape and size of the searchcoil. Understanding the purposes behind the various sizes and shapes of searchcoils will empower you with the ability to choose the best coil for each application. HOW SEARCHCOILS WORK SEARCHCOIL DEPTH SEARCHCOIL SIZES
Garrett is the global leader of ground search metal detectors, pinpointers, coils, and other accessories. Browse Garrett detectors and more. Wednesday, February 08 2023
Grab your Garrett metal detector and accessories and head to Canton, Texas, April 14-16 for their Memorial Hunt! Ti Details: Friday, April 14, through Sunday, April 16 in conjunction with Texas Association of Metal Detecting Clubs (TAMDC). The event will be held at: First Monday (flea market grounds) 800 First Monday Lane Canton, TX 75103 Basic Hunt Package:
Plenty of Fun for All Ages!
Whether it's time to buy your first Garrett metal detector, an upgraded model, or additional coils, headphones, carry bag or other accessories, check out the selection of Garrett treasure hunting items here. Saturday, November 19 2022
If you’re used to water mining, having success in the desert might seem challenging— that is until you start thinking of desert ground During a river high-water event in a non-arid area, gold is moved over a larger area by massive water flows that continue until the water slows as the source dissipates its energy. Spring snow runoff is a good example. Rivers rise and sometimes flood based on the upstream water source. When the snow has melted, the river will slowly get back to normal. In the desert, gold is moved in the exact same way with the exception that water powerful enough to move gold does so and then just simply stops. In a flash flood, gold is moved very violently and often a very short distance, sometimes percolating into valuable pockets. Here’s where the difference between water and desert mining principles comes into play generally flood gold will concentrate in areas that do not meet the standard thought of inside bends and where the water flow becomes lower. For the most part, desert mining experts recommend staying out of the washes, gulches and dry river beds— that is unless you clearly see exposed bedrock. Gold will settle fairly quickly when it is trapped behind jagged bedrock and small fault lifts that have not been worn down over time by constant water flow. It IS true you can find areas of concentrated gold-bearing material in the washes, however, the amount of time and energy to get through feet of overburden is usually just not worth it, especially when there are higher values to be found outside of the wash. Follow the leads out of the wash to where the gold lives in higher concentration. Test and sample areas you see with a great deal of runoff from a tributary coming into the main wash. Here you are only digging through the current flood layer and testing for flood gold. Make your way out of the wash carefully looking at the bottom of the tributary and the areas where the water flowed into the tributary. Look closely for jagged bedrock and slight lifts in the ground and then prospect. Continue to test each of those spots. What started as a few specks of flood gold in the main wash can lead to larger and larger deposits on the flats or in slight inclines across the desert floor. Keep in mind that when a flash flood is dissipating, there is not enough energy to move a lot of rock, but the sand will continue to flow a bit, creating great clues. In general, cool season precipitation (October through April) is the most extensive source of rain in the desert regions. Rainfall is more widespread and of relatively long duration during the cool season. On the other hand, warm season precipitation (May through September) results largely from short monsoon-type thunderstorms. If you’re ready to head to a sunnier climate this winter, keep these tips in mind and you just might find enough similarities between water and desert mining to make you return every year. Good luck! Friday, September 30 2022
In an area either rumored or known to hold gold, where should you look first? The creek, the surrounding hills, washouts, or just where? The characteristics of the gold in that area will help you to know where to start. If the gold is flat and pounded, that indicates it’s been in the water a long time. If the gold is coarse and chunky, you know you’re getting closer to the source. When gold is smoother, stop and go back to the coarsest gold and start working upwards until you find the source.
Keep in mind that gold is gold, so there isn’t necessarily a better type of gold. Some is just easier to recover. There are only two types  of gold deposits. The first type is “lode” which is simply everything that is still in the matrix and in the ground, and the other is “placer” —or everything else. of gold deposits. The first type is “lode” which is simply everything that is still in the matrix and in the ground, and the other is “placer” —or everything else.Lode deposits refer to gold that is still locked within its original solid rock formation. This formation of gold generally starts as a vein in rock and is formed over millions of years. Since the gold is locked up in rock, and can be mixed with quartz, calcite, pyrite, and other minerals, lode gold usually requires specialized mining techniques to extract. Lode mining takes a lot more equipment and generally a lot more expense and is usually undertaken by large commercial operations instead of the average prospector. Placer gold is the gold that most prospectors are more familiar with. Placer gold isn’t really any different than lode gold. It is simply a concentration of that same gold that has eroded and traveled away from the vein. Since gold is very dense, it will move downhill much slower than the surrounding sediment. It tends to become concentrated on or near the surface of the lode, forming a “residual placer” close to the original bedrock exposure. Gold found downhill from the immediate outcrop above the nearest watercourse is called an “eluvial placer.” Once it reaches the nearest waterway and is transported by flowing water, the gold now is known as “alluvial placer.” The origin of the dust, flakes and nuggets found by panning and sluicing is usually from a vein up on a nearby mountain. Bench placers were originally stream placers. Benches are simply where the water used to be, maybe even millions of years ago. They are formed by erosion or geological events such as uplifts, earthquakes or plate drops that changed the stream flow. Some of the most profitable mining is performed on benches. Many benches are highly concentrated by the alluvial deposits that still feed them. Stream deposits are the last resting place for gold. Once the gold has been released from the lode, gravity and nature does the rest. And unless gold gets stranded on a bench, it will find its way to the water someday. It may take a million years, but it will get there. When deciding where to begin prospecting, most of the time you’ll want to start panning in a water way, or a wash in the desert where water once flowed. Then let the gold tell you where to go from there. When the gold gets coarse and ragged, start to move up, looking in reverse of how it got to the spot where you found it. In addition to panning and sluicing you may wish to upgrade your mining efforts with a highbanker or power sluice, dredge or trommel. Moving soft soil or river gravel is obviously much easier than breaking rock, but for small scale miners, a rock crusher can pulverize 2 or 3 inch sized rocks into powder in no time. Move more material faster— get more gold! Thursday, September 22 2022
Gold can hide down in the deepest part of a crack or crevice or behind a boulder and often is best reached with a hand dredge, also called a "sucker gun" or "suction gun." This gold prospecting tool is ideal for working below the water line when a motorized dredge cannot be used. It helps you get the gold out of some really tight spaces, a hand dredge is well, handy, when you're prospecting along a river. If you've found a rich spot that is hard to access, these two hand dredges can produce some decent gold! Also check out the many accessories that make your hand dredge even better!
Clamps are not necessary unless you plan to use the system in strong current and want to be extra cautious. For users in deeper water or stronger current, consider wrapping a leash around the lid and tie it off at your waist to prevent the bucket from breaking away.
The Quick Sniper is a tool that uses some new ideas to help you collect the hard-to-get gold from heavy sands under boulders, in crevices, and behind obstructions. The “NOZZLE” of the Quick-Sniper is where the magic happens. Inside the nozzle is a short white plastic pipe that extends into the tube. This allows you to pump the handle four or five times before you need to take steps to collect sand and gravel. Instead of pulling the handle and then ejecting the material into a pan or bucket after each pull, the cavity created inside the tube will hold your heavies, allowing water and the lightest material to swirl out and go back into the water before you pull again. Shaking the pump gently will transfer the heaviest of sands and gravel deeper into the cavity. Then, after you have repeated this action a few times, pull off the cap and dump the contents of the pump into your pan or bucket. The flexible tube extending from the end of the nozzle is designed to pull out, allowing you to extend the reach of the tube about 4-5 inches. If this tube is sliding too easily, wrap some electrical tape around the inner end, and it will be more secure within the Quick-Sniper.
Thursday, April 28 2022
Over the years, metal detecting has continued to become one of the most popular forms of gold prospecting, especially with folks new to prospecting. Panning, sluicing, and highbanking can be lucrative ways to recover the shiny stuff, but when you’re first bitten by the gold bug, you might opt for the simplest, quickest approach — swinging a detector. Not only is it physically easier than processing heavy dirt and rock, it offers the added bonus of finding more than just gold, such as coins, jewelry, relics, and other buried metallic treasures, too. Aside from record gold prices, another reason that people are eager to try metal detecting i The basic premise of metal detecting is allowing the detector to introduce an energy field into the ground, and allowing that field the opportunity to return any target information that it finds via the detector’s control box. The two most common types of metal detectors to consider: VLF (very low frequency) metal detectors are the most common type of detector. They work by sending out energy that is either reflected off or conducts through an object containing metal. The device then measures how long it takes for the signal to return. Frequency refers to how fast a metal detector sends signals into the ground. As the name indicates, these detectors use very low frequency coils (generally below 30 kHz.) The outer coil serves as the transmitter and the inner coil serves as a receiver. PI (pulse induction) metal detectors send energy into the ground and measure the decay of that signal. Anything that slows or speeds the decaying signal is a target. This technology sends powerful, short bursts (pulses) of current through a coil of wire. Each pulse generates a brief magnetic field. When the pulse ends, the magnetic field reverses polarity and collapses very suddenly, resulting in a sharp electrical spike. This spike lasts a few microseconds (millionths of a second) and causes another current to run through the coil. This current is called the reflected pulse and is extremely short, lasting only about 30 microseconds. Another pulse is then sent and the process repeats. Generally speaking, the higher the price of a metal detector, the more features it will have. More features translate into more knobs. The more features and/or knobs that a detector has, the more you are able to tune the metal detector to the type of hunting conditions that you are likely to encounter. With that being said, the downside to a large number of features is that even though you are able to fine tune the detector to match the local conditions, there are also more ways of setting up the detector incorrectly. Setting up a machine "wrong" may result in a decrease in depth and sensitivity and your $900 metal detector may be outdone by a $200 model! It is critical to read the owner’s manual that comes with your detector and learn to use it properly for maximum results. Keep in mind when shopping for a detector that gold detectors are not necessarily higher in cost, but they are built with a higher sensitivity to detecting gold nuggets, have better ground balancing and discrimination abilities, and could be the best option for you. The #1 question that everyone asks is “What is the best metal detector?” Unfortunately, there is no one single answer. Each metal detectorist has specific needs that cannot be met by one single detector. The easiest way to find the "best" detector is to evaluate YOUR detecting style, your experience level, what items you hope to find, and the time that you will spend metal detecting. After taking all of these things into consideration, then you will be able to find a metal detector that fits your needs and your budget. If you’re wondering how deep a detector can detect, realize that there are too many variables to be able to unequivocally quote a depth for any particular brand or model. The size of the target, how it is positioned, ground mineralization, ground moisture, and more are just some of the factors that affect the depth of a detector. When treasure hunting with your detector for coins, relics, or jewelry, use your imagination as to where to hunt — anywhere people are likely to have lost something or left something behind is a likely place to dig up good finds—playgrounds at schools and parks, picnic areas, campgrounds, new construction sites, ghost towns, old homesteads, woodlands, plowed fields and pastures, sports fields, showgrounds, and racetracks, swimming holes, beaches, jetties, and piers. Right under your feet might be a good place to start; you never know what you'll find in your own backyard! Remember to always know local laws before using your metal detector. Many state and national parks and historic sites do not permit detecting. Be sure to first ask permission to treasure hunt on private property. If you want to get out there this year and get your share of the gold but the idea of panning, sluicing, highbanking, or using another piece of gold mining equipment just isn't your idea of fun, that's OK. Consider a metal detector instead. Since the lure of uncovering a gold nugget of any size is addictive, you'll see people in known gold bearing areas swinging a detector, listening intently through their headphones for that magic tone that says DIG. Go ahead and join the fun! Today it is easier and more productive than ever to go treasure hunting. The metal detecting hobby has gone to a whole new level using state of the art technology that makes metal detecting equipment more high tech than ever. Saturday, March 26 2022
Gold is gold, so there isn’t necessarily a better type of gold, however, mining for lode gold has many more challenges than mining for placer gold. The formation of gold generally starts as a vein in rock. This is referred to as “lode gold” and is formed when molten rock in the earth’s crust heats groundwater under great pressure. In fractured bedrock with appropriate rock chemistry, super-heated water (hydrothermal) at approximately 400-700 degrees Fahrenheit dissolves certain elements a Placer gold is the gold that most prospectors are more familiar with. Placer gold isn’t really any different than lode gold. It is simply a concentration of gold that is created over time as it erodes from hard rock veins. When exposed at the surface, a mineralized deposit will break down and erode due to reactions with oxygen, water and wind, coupled with temperature fluctuations. Since gold is very dense, it will move downhill much slower than the surrounding sediment. It tends to become concentrated on or near the surface of the lode, forming a “residual placer” close to the original bedrock exposure. Gold found downhill from the immediate outcrop above the nearest watercourse is called an “eluvial placer.” Once it reaches the nearest waterway and is transported by flowing water, the gold now forms an “alluvial placer.” The origin of the dust, flakes and nuggets found by panning and sluicing is usually from a vein up on a nearby mountain. An ore body is a mineral deposit that can be mined, processed and sold at a profit. All ore bodies are deposits. Few deposits are actual ore bodies. Valuable gold deposits in placers are referred to as “pay streaks” instead of ore bodies. Over time, eluvial and alluvial placers can become covered with sediment. When buried long enough and deep enough, these deposits will turn into “fossil placers.” Sometimes the fossil placers are re-cemented into sandstone or conglomerate rock and then must be mined using hard rock techniques. Hard rock ores have mostly fine to micro-fine gold in solid rock; placers contain fine to coarse gold particles in a softer bulk material or matrix. That makes placers much easier to mine and process. Moving soft soil or river gravel is obviously much easier than breaking rock. For small scale miners, though, a rock crusher can pulverize 2 or 3 inch sized rocks into powder in no time! But for the average prospector, panning and sluicing will be more fun and more profitable, and as time goes on, you may wish to upgrade your mining efforts with a highbanker or power sluice, dredge or trommel. Good luck! Monday, February 21 2022
Depending on where you live and where you like to treasure hunt, you might still be buried under feet of snow. Or maybe spring has sprung and temperatures are on the rise there. No matter the weather, you probably have extra time on your hands this time of year, so put that time to good use. Even though you might not have been out in the field for the last few months, you can still be prospecting and getting prepared for a new season of gold hunting! In other words, use your downtime wisely, so you can hit the ground running as soon as Mother Nature allows. Inspect equipment. Did you properly clean and store your sluice and/or highbanker at the end of last season? In advance of heading Prepare your tools. Sharpen digging tools, picks, shovels, chisels and other specialty tools that require sharp edges. Now is also a good time to mark screwdrivers, magnets, crevice tools and other small implements with some bright colored paint. It’s amazing how easily tools can get “lost” in the dirt. A strip of bright yellow or red can help you more easily spot them. Double check the seals on snuffer bottles, hand dredges, and vials to make sure they’re tight. Pack your backpack or tool kit with everything necessary for a full day’s work. Maintain your metal detector. If your metal detector is still under warranty or giving hints of potential issues, the off-season is ideal for sending it to the manufacturer or taking it to an authorized repair shop to be fixed or tuned up. Check your rechargeable battery and make sure it is fully charged. Better yet, purchase a new battery as a back up. It’s also time to dust off the operator manual or search YouTube for “how to” videos pertaining to your brand and model. You’ll likely uncover some helpful tips and tricks, or learn a new recovery method. Is this the year to add a new coil or pinpointer? Now is a good time to consider upgrades and make those purchases earlier than you expect to use them. Do your research. The best kind of research brings together different forms of info from a multitude of sources. It is the info gleaned from combined sources that can help you to determine the best possible place to locate precious metal or gems— old mining district reports, mining history books, topo maps, aerial photos. Consult the Bureau of Land Management's LR2000 searchable database. The legacy system is undergoing upgrades; as the new systems is implemented, information will be easier to find. It can take a lot of time to research new areas, but when you find a new spot with good gold, it will be well worth your time and effort! It’s also a good idea to have alternate sites in mind just in case you cannot access your primary sites due to unforeseen closures.
Saturday, November 27 2021
If you’re ready to head to a sunnier climate this winter to do some desert prospecting, understanding the weather a |
|
Nugget of News Blog |






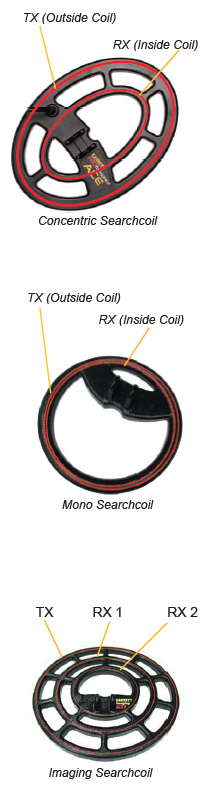 used in as well as the targets being sought. A change in any one of these variables may require a different searchcoil. Sometimes changing the search coil on your metal detector is the next best thing to buying a whole new machine! It is possible that merely changing the coil on your detector will lead you to a host of new targets.
used in as well as the targets being sought. A change in any one of these variables may require a different searchcoil. Sometimes changing the search coil on your metal detector is the next best thing to buying a whole new machine! It is possible that merely changing the coil on your detector will lead you to a host of new targets.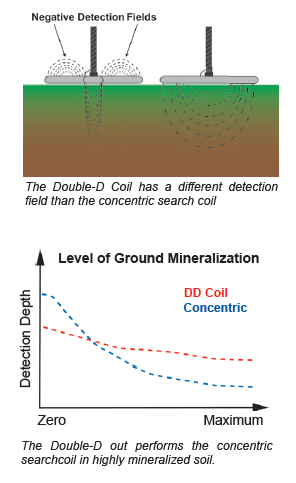 significantly reduce ground interference and, thereby, recover the performance lost by a concentric coil over mineralized soil. With the Double-D, it is the arrangement of the TX and RX coils that produce a canceling effect of ground signals. This configuration is called DD because both TX and RX coils are in the shape of a “D”. The positive detection fi eld of the DD runs beneath the overlapping center section from front-to-back. The remaining portion of the coil actually produces negative (i.e. canceling) detection fields. It is this canceling field that allows the DD coil to maintain performance over mineralized ground. Because of its small positive detection field, the DD is inherently less sensitive than a concentric searchcoil of the same size, over non-mineralized ground. The Double-D will, however, significantly outperform the concentric coil over mineralized ground. For this reason, it is highly recommended when hunting over mineralized ground commonly found when prospecting and relic hunting.
significantly reduce ground interference and, thereby, recover the performance lost by a concentric coil over mineralized soil. With the Double-D, it is the arrangement of the TX and RX coils that produce a canceling effect of ground signals. This configuration is called DD because both TX and RX coils are in the shape of a “D”. The positive detection fi eld of the DD runs beneath the overlapping center section from front-to-back. The remaining portion of the coil actually produces negative (i.e. canceling) detection fields. It is this canceling field that allows the DD coil to maintain performance over mineralized ground. Because of its small positive detection field, the DD is inherently less sensitive than a concentric searchcoil of the same size, over non-mineralized ground. The Double-D will, however, significantly outperform the concentric coil over mineralized ground. For this reason, it is highly recommended when hunting over mineralized ground commonly found when prospecting and relic hunting.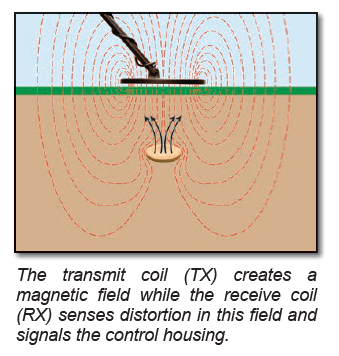

 as a massive sluice box. Many of the principles you’re used to when prospecting and mining in waterways, will translate into desert mining. The most important thing to remember is that water is crucial to gold movement. Unlike a running river or creek with highs and lows, desert placers are much different in that gold is moved quickly during a flash flood, leaving gold stranded as opposed to being moved further by continual water flow in a creek.
as a massive sluice box. Many of the principles you’re used to when prospecting and mining in waterways, will translate into desert mining. The most important thing to remember is that water is crucial to gold movement. Unlike a running river or creek with highs and lows, desert placers are much different in that gold is moved quickly during a flash flood, leaving gold stranded as opposed to being moved further by continual water flow in a creek.


 nd molecules from cubic miles of crust and transports them in a circulation loop. When this hydrothermal solution cools or chemically reacts with local rocks, the elements and molecules will come out of the solution and solidify (precipitate), forming ore deposits. The hydrothermal solution will begin precipitating on the sides of the opening and slowly fill the entire crack over time. This is how gold veins can form. These geologic processes take place over millions of years, and can happen many times over many years in the same location. Since the gold is locked up in rock, it is usually pretty hard to get to— usually requiring specialized mining techniques to mine and extract. Lode mining takes a lot more equipment and generally a lot more expense and is usually undertaken by large commercial operations instead of the average prospector.
nd molecules from cubic miles of crust and transports them in a circulation loop. When this hydrothermal solution cools or chemically reacts with local rocks, the elements and molecules will come out of the solution and solidify (precipitate), forming ore deposits. The hydrothermal solution will begin precipitating on the sides of the opening and slowly fill the entire crack over time. This is how gold veins can form. These geologic processes take place over millions of years, and can happen many times over many years in the same location. Since the gold is locked up in rock, it is usually pretty hard to get to— usually requiring specialized mining techniques to mine and extract. Lode mining takes a lot more equipment and generally a lot more expense and is usually undertaken by large commercial operations instead of the average prospector.
 nd topography can add to your success. Before loading up and heading to the Southwest, only to be disappointed by bad weather, first check out the weather patterns for the last 60 days and the predicted weather for the next 30-60 days. Why is that important? Well, it mostly comes down to rainfall— how much and how fast. For example, if there will be a lot of rainfall over an extended time, soils will be loosened and gravity will do its job and cause deeper, and sometimes more concentrated, pay streaks. In general, cool season precipitation (October through April) is the most extensive source of rain in the desert regions. Rainfall is more widespread and of relatively long duration during the cool season. On the other hand, warm season precipitation (May through September) results largely from convective precipitation in the form of short monsoon-type thunderstorms.
nd topography can add to your success. Before loading up and heading to the Southwest, only to be disappointed by bad weather, first check out the weather patterns for the last 60 days and the predicted weather for the next 30-60 days. Why is that important? Well, it mostly comes down to rainfall— how much and how fast. For example, if there will be a lot of rainfall over an extended time, soils will be loosened and gravity will do its job and cause deeper, and sometimes more concentrated, pay streaks. In general, cool season precipitation (October through April) is the most extensive source of rain in the desert regions. Rainfall is more widespread and of relatively long duration during the cool season. On the other hand, warm season precipitation (May through September) results largely from convective precipitation in the form of short monsoon-type thunderstorms.